通过定时器,我们可以控制计算机在将来指定的某个时刻执行特定的动作。传统的定时器,以时钟滴答(jiffy)作为计时单位,因此它的精度较低(例如HZ=1000时,精度为1毫秒),我们也称之为低精度定时器。
1. 初始化定时器
我们在概述中介绍过,内核中通过init_timer对定时器进行初始化,定时器中最关键的三个信息是:到期时间、到期处理函数、到期处理函数的参数。init_timer宏及定时器结构struct timer_list(取名struct timer可能更合适)的定义如下:
linux/include/linux/timer.h:
#define init_timer(timer) \
__init_timer((timer), 0)
#define __init_timer(_timer, _flags) \
init_timer_key((_timer), (_flags), NULL, NULL)
struct timer_list {
/*
* All fields that change during normal runtime grouped to the
* same cacheline
*/
struct list_head entry; /*用于将当前定时器挂到CPU的tvec_base链表中*/
unsigned long expires; /*定时器到期时间*/
struct tvec_base *base; /*定时器所属的tvec_base*/
void (*function)(unsigned long); /*到期处理函数*/
unsigned long data; /*到期处理函数的参数*/
int slack; /*允许的偏差值*/
...
};
init_timer_key实现时,会将定时器指向执行初始化动作的CPU的tvec_base结构。内核为每个CPU分配一个struct tvec_base对象,用来记录每个CPU上定时器相关的全局信息(我们将在下一节详细说明)。
linux/kernel/timer.c:
/**
* init_timer_key - initialize a timer
* @timer: the timer to be initialized
* @flags: timer flags
* @name: name of the timer
* @key: lockdep class key of the fake lock used for tracking timer
* sync lock dependencies
*
* init_timer_key() must be done to a timer prior calling *any* of the
* other timer functions.
*/
void init_timer_key(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned int flags,
const char *name, struct lock_class_key *key)
{
debug_init(timer);
do_init_timer(timer, flags, name, key);
}
static void do_init_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned int flags,
const char *name, struct lock_class_key *key)
{
struct tvec_base *base = __raw_get_cpu_var(tvec_bases);
timer->entry.next = NULL;
timer->base = (void *)((unsigned long)base | flags);
timer->slack = -1;
...
}
struct tvec_base {
spinlock_t lock; /*同步当前tvec_base的链表操作*/
struct timer_list *running_timer; /*正在运行(到期触发)的定时器*/
unsigned long timer_jiffies; /*用于判断定时器是否到期的当前时间,通常和系统的jiffies值相等*/
unsigned long next_timer; /*下一个到期的定时器的到期时间*/
unsigned long active_timers; /*激活的定时器的个数*/
struct tvec_root tv1; /*tv1~tv5是用于保存已添加定时器的链表,也称为时间轮*/
struct tvec tv2;
struct tvec tv3;
struct tvec tv4;
struct tvec tv5;
} ____cacheline_aligned;
/*
* per-CPU timer vector definitions:
*/
#define TVN_BITS (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 4 : 6)
#define TVR_BITS (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 6 : 8)
#define TVN_SIZE (1 << TVN_BITS)
#define TVR_SIZE (1 << TVR_BITS)
#define TVN_MASK (TVN_SIZE - 1)
#define TVR_MASK (TVR_SIZE - 1)
#define MAX_TVAL ((unsigned long)((1ULL << (TVR_BITS + 4*TVN_BITS)) - 1))
struct tvec {
struct list_head vec[TVN_SIZE];
};
struct tvec_root {
struct list_head vec[TVR_SIZE];
};
2. 添加定时器
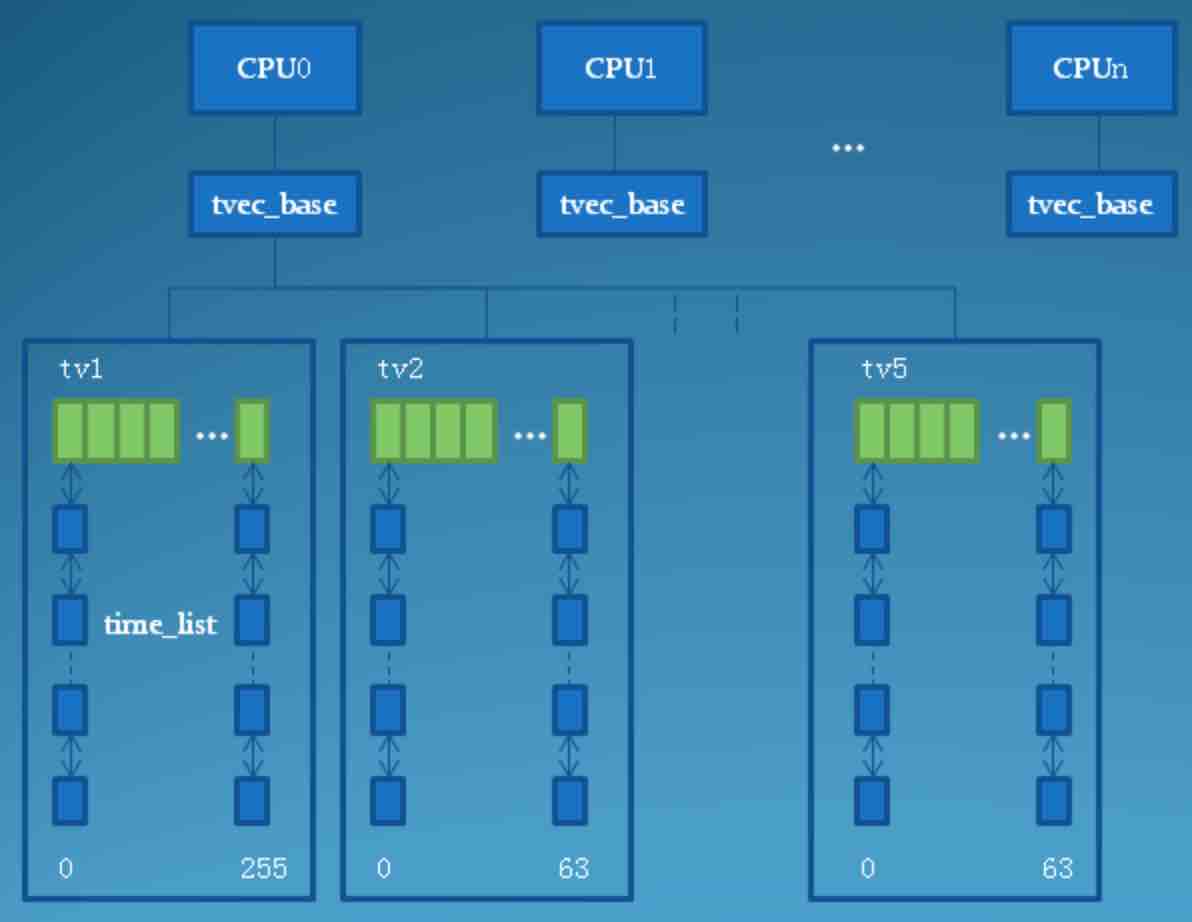
add_timer将定时器添加到执行CPU的tvec_base的时间轮链表中。内核根据定时器到期时间与当前时间jiffies的差值(值越小说明到期时间越早),将定时器分别挂到五个级别的链表数组,级别越低链表到期时间越早,如下表所示:
| 链表数组 | 时间差 |
|---|---|
| tv1 | 0-255(2^8) |
| tv2 | 256–16383(2^14) |
| tv3 | 16384–1048575(2^20) |
| tv4 | 1048576–67108863(2^26) |
| tv5 | 67108864–4294967295(2^32) |
其中tv1的数组大小为TVR_SIZE, tv2 tv3 tv4 tv5的数组大小为TVN_SIZE,根据CONFIG_BASE_SMALL配置项的不同,它们有不同的大小。默认情况下,没有使能CONFIG_BASE_SMALL,TVR_SIZE的大小是256,TVN_SIZE的大小则是64,当需要节省内存空间时,也可以使能CONFIG_BASE_SMALL,这时TVR_SIZE的大小是64,TVN_SIZE的大小则是16,以下的讨论我都是基于没有使能CONFIG_BASE_SMALL的情况。当有一个新的定时器要加入时,系统根据定时器到期的jiffies值和timer_jiffies字段的差值来决定该定时器被放入tv1至tv5中的哪一个数组中,最终,系统中所有的定时器的组织结构如下图所示:
从add_timer代码实现上看,最终会调用__internal_add_timer并根据时间差将定时器加入到合适的链表中:
linux/kernel/timer.c:
static void
__internal_add_timer(struct tvec_base *base, struct timer_list *timer)
{
unsigned long expires = timer->expires;
unsigned long idx = expires - base->timer_jiffies; /*idx即为时间差*/
struct list_head *vec;
if (idx < TVR_SIZE) {
int i = expires & TVR_MASK; /*以超时时间(而非时间差idx)作为索引寻找对应的链表,方便后续的超时处理*/
vec = base->tv1.vec + i;
} else if (idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + TVN_BITS)) {
int i = (expires >> TVR_BITS) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv2.vec + i;
} else if (idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + 2 * TVN_BITS)) {
int i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv3.vec + i;
} else if (idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + 3 * TVN_BITS)) {
int i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + 2 * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv4.vec + i;
} else if ((signed long) idx < 0) {
/*
* Can happen if you add a timer with expires == jiffies,
* or you set a timer to go off in the past
*/
vec = base->tv1.vec + (base->timer_jiffies & TVR_MASK);
} else {
int i;
/* If the timeout is larger than MAX_TVAL (on 64-bit
* architectures or with CONFIG_BASE_SMALL=1) then we
* use the maximum timeout.
*/
if (idx > MAX_TVAL) {
idx = MAX_TVAL;
expires = idx + base->timer_jiffies;
}
i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + 3 * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv5.vec + i;
}
/*
* Timers are FIFO:
*/
list_add_tail(&timer->entry, vec);
}
3. 触发定时器
在时钟中断部分,我们提到过每次中断处理时都会调用run_local_timers进行本地定时器的处理:
linux/kernel/timer.c:
/*
* Called by the local, per-CPU timer interrupt on SMP.
*/
void run_local_timers(void)
{
...
raise_softirq(TIMER_SOFTIRQ); /*最终在中断返回时进入软中断处理函数run_timer_softirq*/
}
/*
* This function runs timers and the timer-tq in bottom half context.
*/
static void run_timer_softirq(struct softirq_action *h)
{
struct tvec_base *base = __this_cpu_read(tvec_bases);
...
if (time_after_eq(jiffies, base->timer_jiffies)) /*实际当前时间晚于base中记录的当前时间,说明需要更新base中时间或者有定时器到期*/
__run_timers(base);
}
定时器的到期处理逻辑中,总是先处理tv1中的定时器,如果tv1中所有的链表为空,再从tv2中移动链表并重新添加到tv1中;如果tv1和tv2中为空,再从tv3中移动链表重新添加到tv1和tv2中;依此类推。代码实现如下:
linux/kernel/timer.c:
/**
* __run_timers - run all expired timers (if any) on this CPU.
* @base: the timer vector to be processed.
*
* This function cascades all vectors and executes all expired timer
* vectors.
*/
static inline void __run_timers(struct tvec_base *base)
{
struct timer_list *timer;
spin_lock_irq(&base->lock);
while (time_after_eq(jiffies, base->timer_jiffies)) {
struct list_head work_list;
struct list_head *head = &work_list;
int index = base->timer_jiffies & TVR_MASK; /*以base中的当前时间为索引取出已到期的定时器*/
/*
* Cascade timers:
*/
/*如果低级链表为空,则从高级别链表中移动添加到低级别中*/
if (!index &&
(!cascade(base, &base->tv2, INDEX(0))) &&
(!cascade(base, &base->tv3, INDEX(1))) &&
!cascade(base, &base->tv4, INDEX(2)))
cascade(base, &base->tv5, INDEX(3));
++base->timer_jiffies; /*累加base中当前时间*/
list_replace_init(base->tv1.vec + index, &work_list);
/*处理已到期的定时期的回调函数*/
while (!list_empty(head)) {
void (*fn)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
bool irqsafe;
timer = list_first_entry(head, struct timer_list,entry);
fn = timer->function;
data = timer->data;
irqsafe = tbase_get_irqsafe(timer->base);
timer_stats_account_timer(timer);
base->running_timer = timer;
detach_expired_timer(timer, base);
if (irqsafe) {
spin_unlock(&base->lock);
call_timer_fn(timer, fn, data);
spin_lock(&base->lock);
} else {
spin_unlock_irq(&base->lock);
call_timer_fn(timer, fn, data);
spin_lock_irq(&base->lock);
}
}
}
base->running_timer = NULL;
spin_unlock_irq(&base->lock);
}
#define INDEX(N) ((base->timer_jiffies >> (TVR_BITS + (N) * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK)
static int cascade(struct tvec_base *base, struct tvec *tv, int index)
{
/* cascade all the timers from tv up one level */
struct timer_list *timer, *tmp;
struct list_head tv_list;
list_replace_init(tv->vec + index, &tv_list);
/*
* We are removing _all_ timers from the list, so we
* don't have to detach them individually.
*/
list_for_each_entry_safe(timer, tmp, &tv_list, entry) {
BUG_ON(tbase_get_base(timer->base) != base);
/* No accounting, while moving them */
__internal_add_timer(base, timer);
}
return index;
}
转载请注明:吴斌的博客 » 【时间子系统】四、低精度定时器
